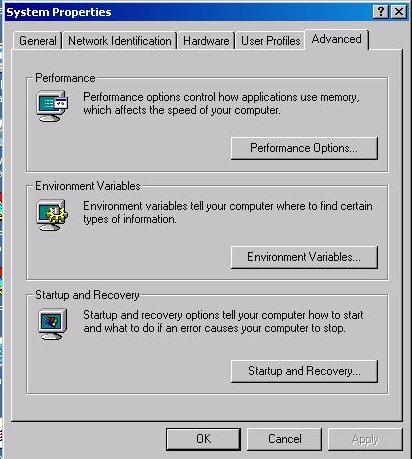
In WINDOWS 2000 you do not use AUTOEXEC.BAT file. Instead you create environment variables. On your computer desktop right click the My Computer icon and select Properties.
On the System Properties window select Advance tab.
On Windows 7 select Start, right click Computer. Click Advance System setting on System properties window select Advance tab, Click Environment Variables button
On Windows XP, to get to the same System Properties window, select Start, Select Control panel,
In the opened Control panel select Performance and Maintenance (it is ar the bottom),
Select System, Advance tab.
Click the Environmental Variables button. Environment Variables window displays.
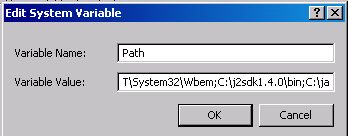
Click New button in System variables frame at the bottom of the Environment Variables Window. For Java SDK enter Path environment variable and.
enter path to JAVA bin folder on your PC. On mine it is C:\j2sdk1.4.0\bin. Type semicolon at the end. If you installed tomcat after java type path to tomcat bin folder on your PC. On mine it is C:\j2sdk1.4.0\bin;C:\jakarta-tomcat-4.1.29\bin;. Do not forget to type semicolon. Click OK button. Click OK button on Environment Variables window. Click OK button on Properties window.
To execute Java program create CLASSPATH environment variable.
For Tomcat enter CATALINA_HOME environment variable name and path to the folder where your tomcat installed. On mine it is C:\jakarta-tomcat-4.1.29
To run Tomcat you need to create JAVA_HOME environment variable. To check your configuration for Tomcat go to C:\jakarta-tomcat-4.1.29\bin directory, type startup and press enter.
Tomcat starts in separate command prompt window.
If Tomcat does not start, probably you have not enough memory set in command prompt. Go to command prompt menu on your desktop and right click it
From drop down menu select properties. Select memory tab. Increase convention memory and click OK to save changes.
Close command prompt if you had it open. Open again and try to start Tomcat.
Now it should be started. To make sure that Tomcat is running properly, open Internet Explored and type URL address:
http://localhost:8080
Tomcat home page displays.